CLINICAL EFFICACY
Only MAVENCLAD can deliver proven efficacy over 96 weeks with a maximum of 10 days of treatment a year for 2 years.1,2
Screening and monitoring should be performed before, during, and after treatment. Each treatment week, taken about a month apart, consists of 1 or 2 MAVENCLAD pills a day for 4 or 5 days in a row. Dosing depends on weight.
ARR: MAVENCLAD significantly reduced ARR vs placebo1,2
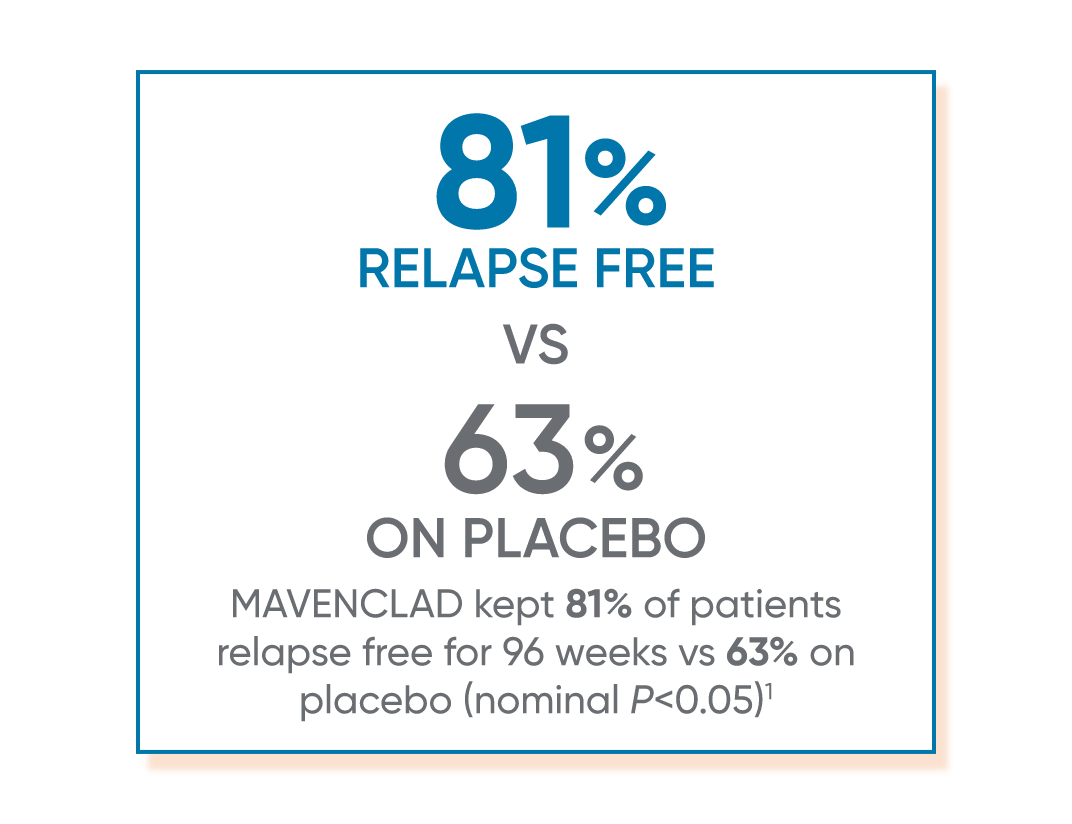
In CLARITY, MAVENCLAD significantly reduced the annualized relapse rate vs placebo at 96 weeks.1,2
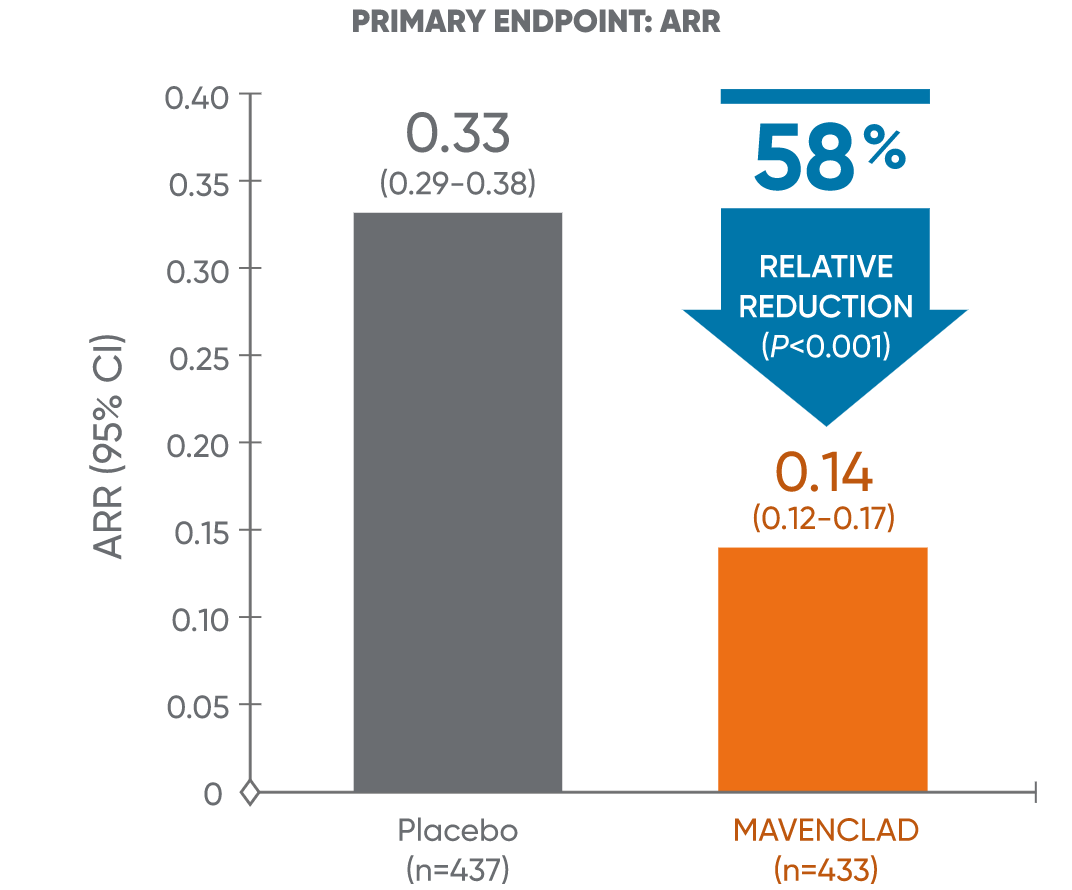
ARR: annualized relapse rate; CI: confidence interval; CLARITY: CLAdRIbine Tablets treating multiple sclerosis orallY.
EDSS: MAVENCLAD significantly reduced EDSS progression vs placebo1,2
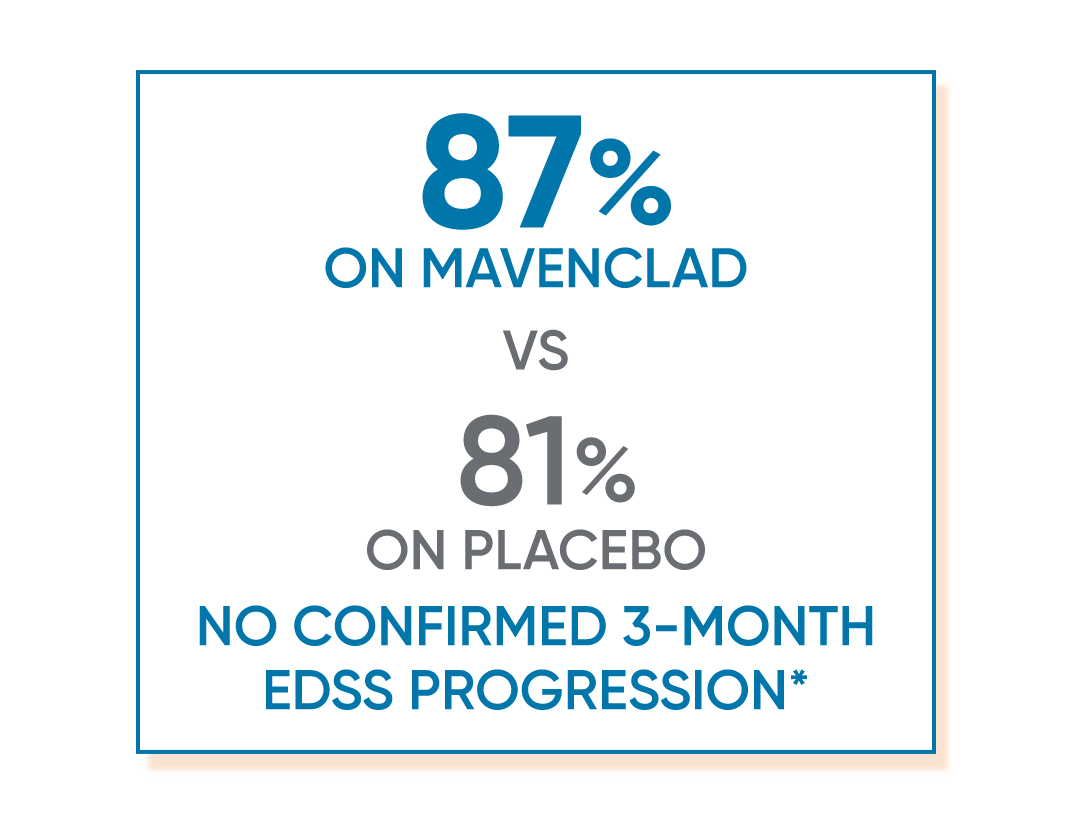
In CLARITY, MAVENCLAD significantly reduced the risk of 3-month confirmed EDSS progression vs placebo.1,2
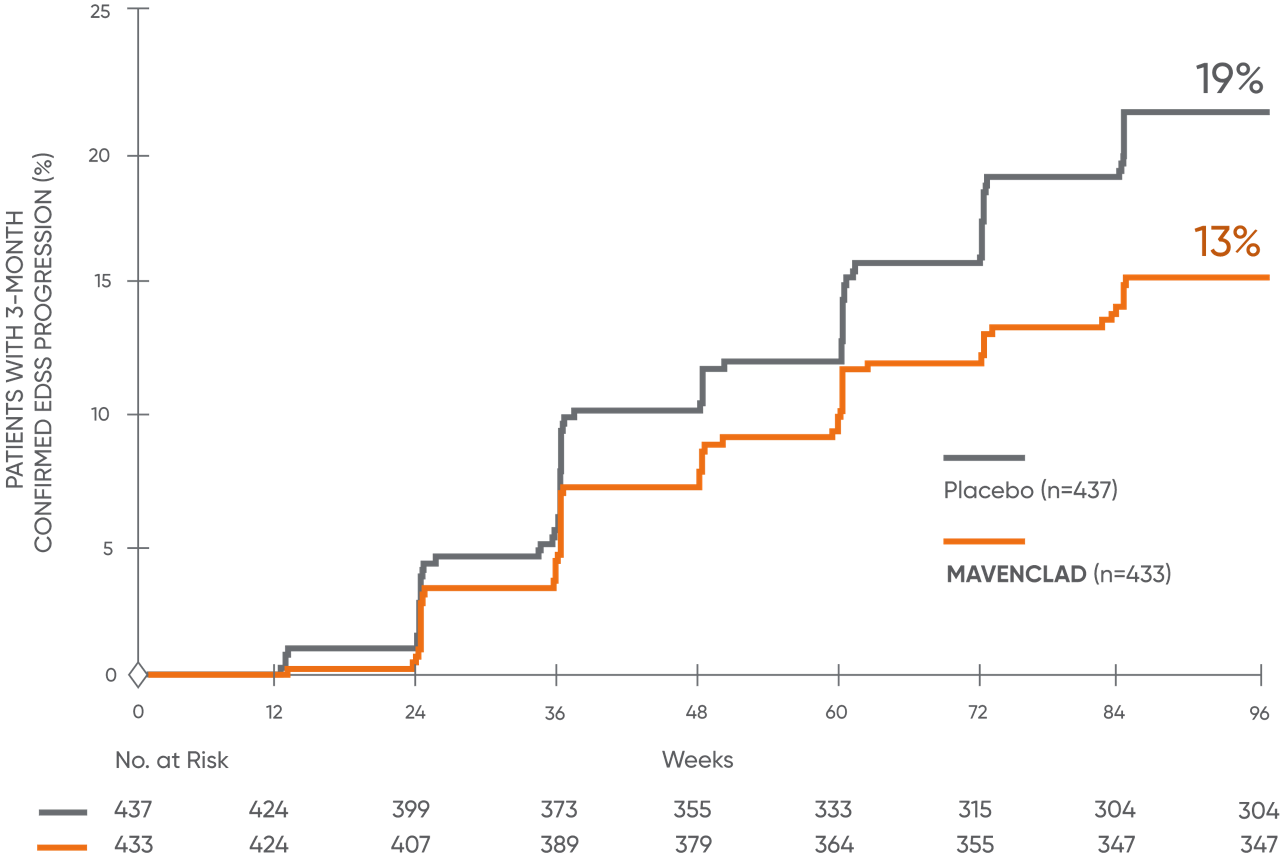

Disability progression was measured in terms of a 3-month sustained change in EDSS score of ≥1 point, if baseline EDSS score was between 0.5 and 4.5 inclusively, or ≥1.5 points if the baseline EDSS score was 0, or ≥0.5 point if the baseline EDSS score was ≥5, over a period of at least 3 months.2
*Proportion of patients with 3-month EDSS progression (MAVENCLAD 13% vs placebo 19%).1
CI: confidence interval; CLARITY: CLAdRIbine Tablets treating multiple sclerosis orallY; EDSS: Expanded Disability Status Scale; HR: hazard ratio.
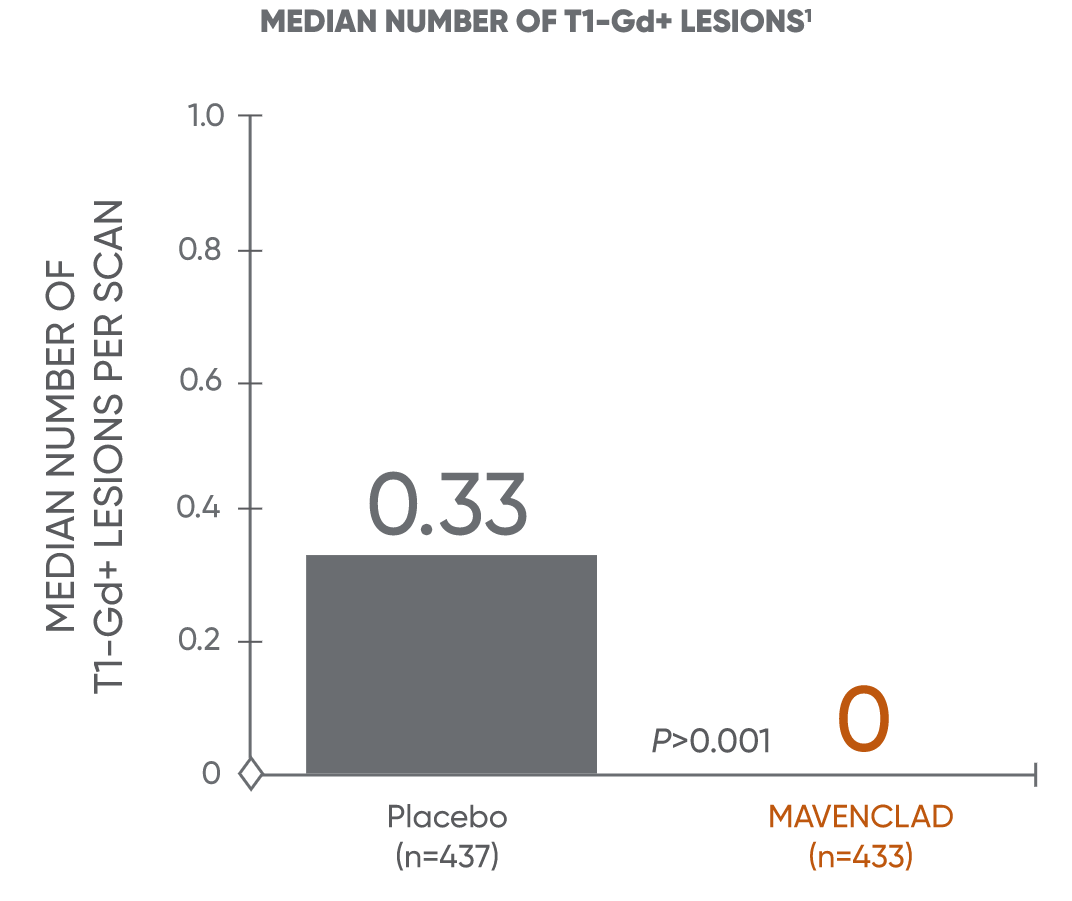
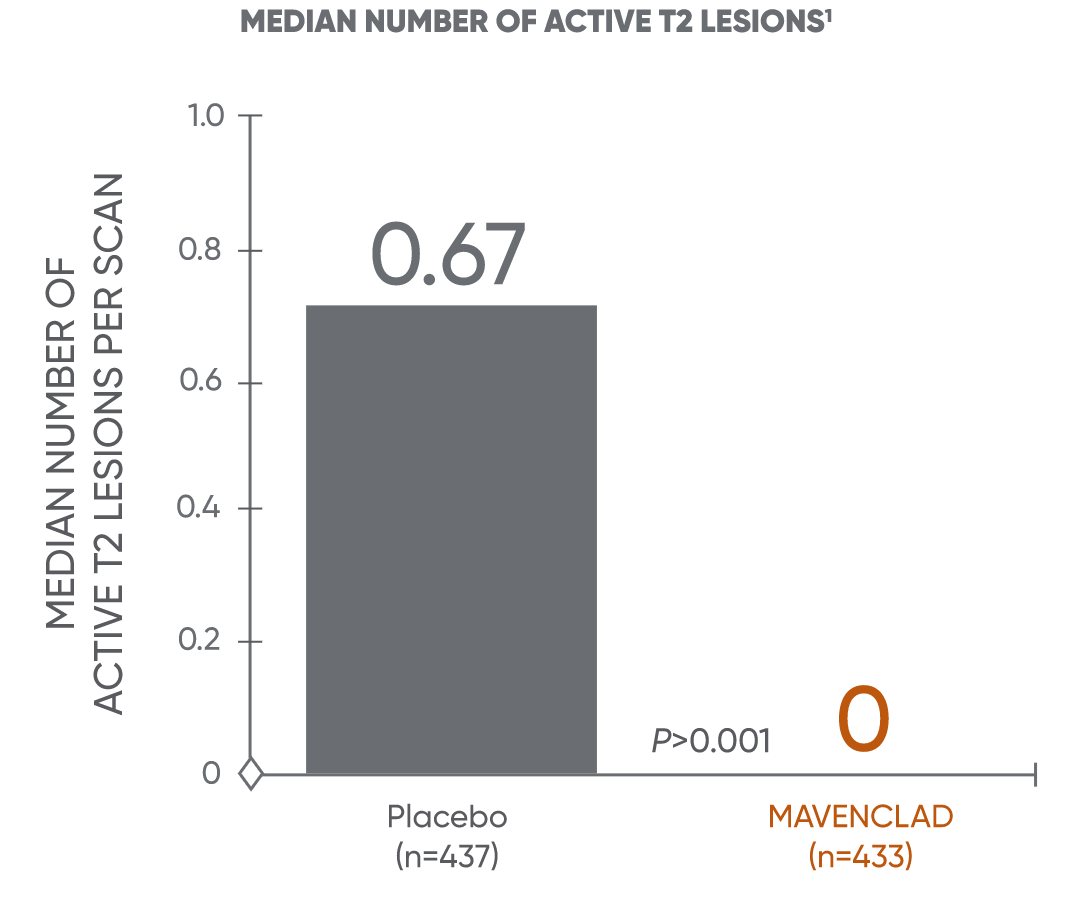
MAVENCLAD significantly reduced the median and mean number of lesions across MRI endpoints vs placebo1
MAVENCLAD demonstrated a significant reduction in mean and median numbers of active T1-Gd+ and active T2 lesions at 2 years vs placebo.1,2
Median lesion reduction
Mean lesion reduction
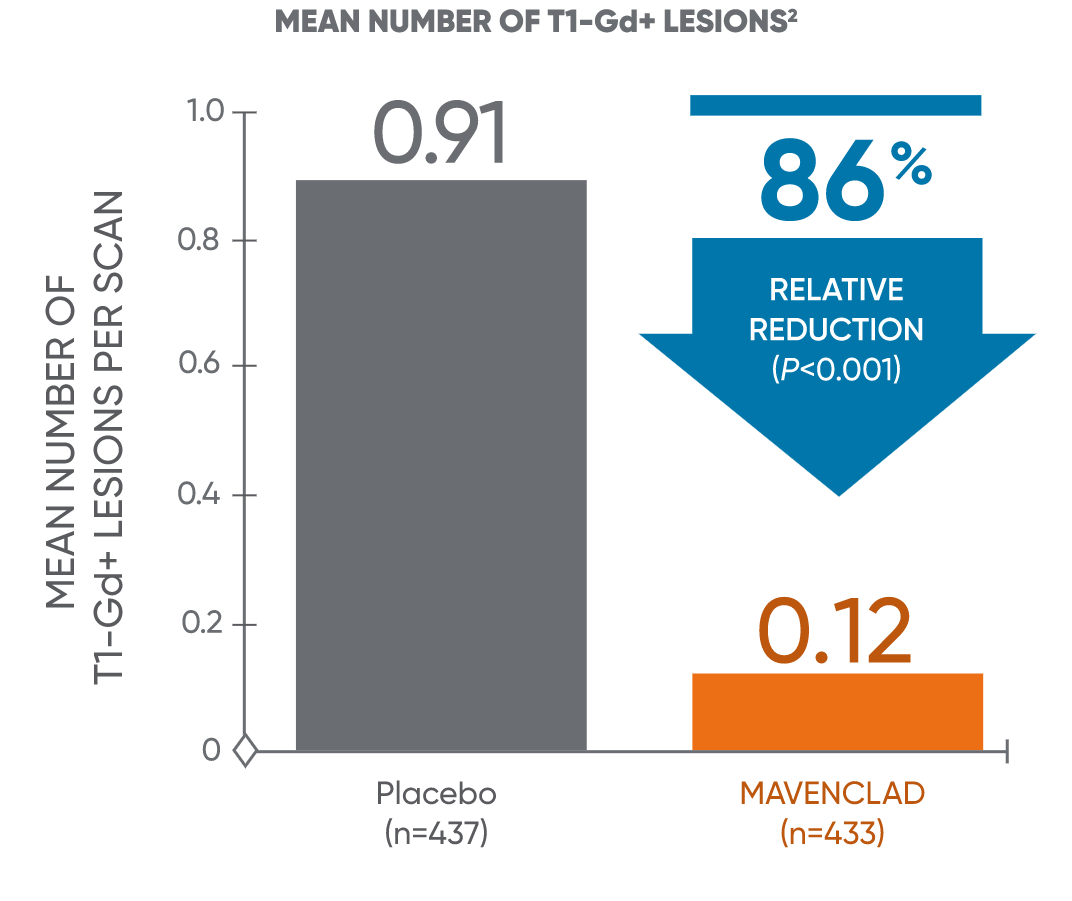
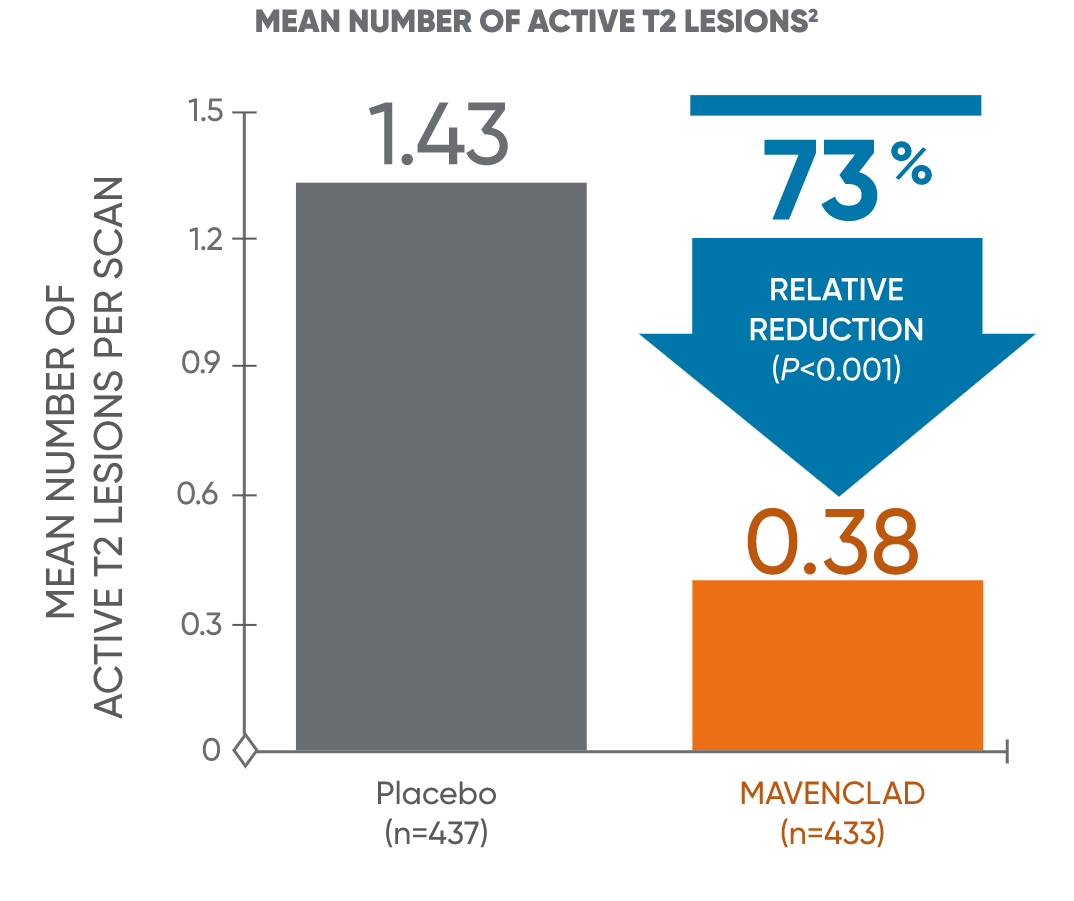
The mean relative reduction reflects that not all patients had lesions at 96 weeks compared to placebo. Patients taking MAVENCLAD had fewer T1-Gd+ lesions: 13.2% taking MAVENCLAD vs 51.7% on placebo. Patients taking MAVENCLAD had fewer active T2 lesions: 38.3% taking MAVENCLAD vs 71.6% on placebo.2,3
CLARITY: CLAdRIbine Tablets treating multiple sclerosis orallY; T1-Gd+: T1 gadolinium-enhanced.
INDICATION and IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION for MAVENCLAD® (cladribine) tablets
MAVENCLAD® (cladribine) is indicated for the treatment of relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS), to include relapsing-remitting disease and active secondary progressive disease, in adults. Because of its safety profile, use of MAVENCLAD is generally recommended for patients who have had an inadequate response to, or are unable to tolerate, an alternate drug indicated for the treatment of MS.
Limitations of Use: MAVENCLAD is not recommended for use in patients with clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) because of its safety profile.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
WARNING: MALIGNANCIES and RISK OF TERATOGENICITY
- Treatment with MAVENCLAD may increase the risk of malignancy. MAVENCLAD is contraindicated in patients with current malignancy. In patients with prior malignancy or with increased risk of malignancy, evaluate the benefits and risks of the use of MAVENCLAD on an individual patient basis. Follow standard cancer screening guidelines in patients treated with MAVENCLAD.
- MAVENCLAD is contraindicated for use in pregnant women and in women and men of reproductive potential who do not plan to use effective contraception because of the potential for fetal harm. Malformations and embryolethality occurred in animals. Exclude pregnancy before the start of treatment with MAVENCLAD in females of reproductive potential. Advise females and males of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during MAVENCLAD dosing and for 6 months after the last dose in each treatment course. Stop MAVENCLAD if the patient becomes pregnant.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Patients with current malignancy.
- Pregnant women, and women and men of reproductive potential who do not plan to use effective contraception during and for 6 months after the last dose in each treatment course. May cause fetal harm.
- Patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
- Patients with active chronic infections (e.g., hepatitis or tuberculosis).
- Patients with a history of hypersensitivity to cladribine.
- Women intending to breastfeed on a MAVENCLAD treatment day and for 10 days after the last dose.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Malignancies: Treatment with MAVENCLAD may increase the risk of malignancy. After the completion of 2 treatment courses, do not administer additional MAVENCLAD treatment during the next 2 years. In clinical studies, patients who received additional MAVENCLAD treatment within 2 years after the first 2 treatment courses had an increased incidence of malignancy. The risk of malignancy with reinitiating MAVENCLAD more than 2 years after the completion of 2 treatment courses has not been studied. Follow standard cancer screening guidelines in patients treated with MAVENCLAD.
- Risk of Teratogenicity: MAVENCLAD may cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women. In females of reproductive potential, exclude pregnancy before initiation of each treatment course of MAVENCLAD and prevent by the use of effective contraception during MAVENCLAD dosing and for at least 6 months after the last dose of each treatment course. Women who become pregnant during treatment with MAVENCLAD should discontinue treatment.
- Lymphopenia: MAVENCLAD causes a dose-dependent reduction in lymphocyte count. Concomitant use of MAVENCLAD with hematotoxic drugs may increase the risk of adverse reactions because of the additive hematological effects. Monitor lymphocyte counts before, during, and after treatment.
- Infections: Serious, including life-threatening or fatal, infections have occurred. MAVENCLAD reduces the body's immune defense, and an increased risk of infections has been observed in patients receiving MAVENCLAD. Infections occurred in 49% of MAVENCLAD-treated patients compared to 44% of patients treated with placebo in clinical studies; serious or severe infections occurred in 2.4% of MAVENCLAD- treated patients and 2.0% of placebo-treated patients. The most frequent serious infections included herpes zoster and pyelonephritis. Fungal infections were observed, including cases of coccidioidomycosis. Single fatal cases of tuberculosis and fulminant hepatitis B were reported in the clinical program.
- Screen patients for active and latent infections (tuberculosis, hepatitis B or C). Delay treatment until infection is fully resolved or controlled.
- Vaccinate patients who are seronegative for varicella zoster virus (VZV) prior to treatment. Vaccinate patients who are seropositive to VZV with recombinant, adjuvanted zoster vaccine either prior to or during treatment, including when their lymphocyte counts are less than or equal to 500 cells per microliter.
- Administer anti-herpes prophylaxis in patients with lymphocyte counts less than 200 cells per microliter. Monitor for infections.
- Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) has been reported in patients treated with parenteral cladribine for oncologic indications. No case of PML has been reported in clinical studies of cladribine in patients with MS. Obtain a baseline magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) within 3 months before initiating the first treatment course of MAVENCLAD. At the first sign of PML, withhold MAVENCLAD and perform an evaluation.
- Administer all immunizations (except as noted for VZV) according to immunization guidelines prior to starting MAVENCLAD. Administer live-attenuated or live vaccines at least 4 to 6 weeks prior to starting MAVENCLAD due to risk of infection.
- Hematologic Toxicity: In addition to lymphopenia, decreases in other blood cells and hematological parameters have been reported with MAVENCLAD in clinical studies. Obtain complete blood count (CBC) with differential including lymphocyte count before and during treatment, periodically thereafter, and when clinically indicated.
- Graft-versus-Host Disease with Blood Transfusions: Transfusion-associated graft-versus-host disease has been observed rarely after transfusion of nonirradiated blood in patients treated with cladribine for non-MS treatment indications. In patients who require blood transfusion, irradiation of cellular blood components is recommended.
- Liver Injury: In clinical studies, 0.3% of MAVENCLAD-treated patients had liver injury (serious or causing treatment discontinuation) compared to 0 placebo patients. Obtain serum aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase, and total bilirubin levels prior to treatment. Discontinue MAVENCLAD if clinically significant liver injury is suspected.
- Hypersensitivity: If a hypersensitivity reaction is suspected, discontinue MAVENCLAD therapy. Do not use MAVENCLAD in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to cladribine.
- Cardiac Failure: In clinical studies, one MAVENCLAD-treated patient experienced life-threatening acute cardiac failure with myocarditis, which improved after approximately one week. Cases of cardiac failure have also been reported with parenteral cladribine used for treatment indications other than multiple sclerosis. Instruct patients to seek medical advice if they experience symptoms of cardiac failure (e.g., shortness of breath, rapid or irregular heartbeat, swelling).
Adverse Reactions: The most common adverse reactions (incidence of >20%) are upper respiratory tract infection, headache, and lymphopenia.
Drug Interactions: Concomitant use with immunosuppressive or myelosuppressive drugs and some immunomodulatory drugs (e.g., interferon beta) is not recommended and may increase the risk of adverse reactions. Acute short-term therapy with corticosteroids can be administered. Monitor for additive effects on the hematological profile with use of hemotoxic drugs. Avoid concomitant use of antiviral and antiretroviral drugs. Avoid concomitant use of BCRP or ENT/CNT inhibitors as they may alter bioavailability of MAVENCLAD.
Use in Specific Populations: Studies have not been performed in pediatric, or elderly patients >65 years, pregnant or breastfeeding women. Use in patients with moderate to severe renal or hepatic impairment is not recommended.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact EMD Serono, Inc. at 1-800-283-8088 ext. 5563 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Please see FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION, including BOXED WARNING.