MAVENCLAD selectively depletes lymphocytes.6,7 Two months after administration, most immune cells begin to recover toward normal levels.3,8
The proposed mechanism by which MAVENCLAD exerts its therapeutic effects (MAVENCLAD MOA) in patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) is not fully elucidated but is thought to involve cytotoxic effects on B and T lymphocytes through impairment of DNA synthesis, resulting in depletion of lymphocytes.5,6
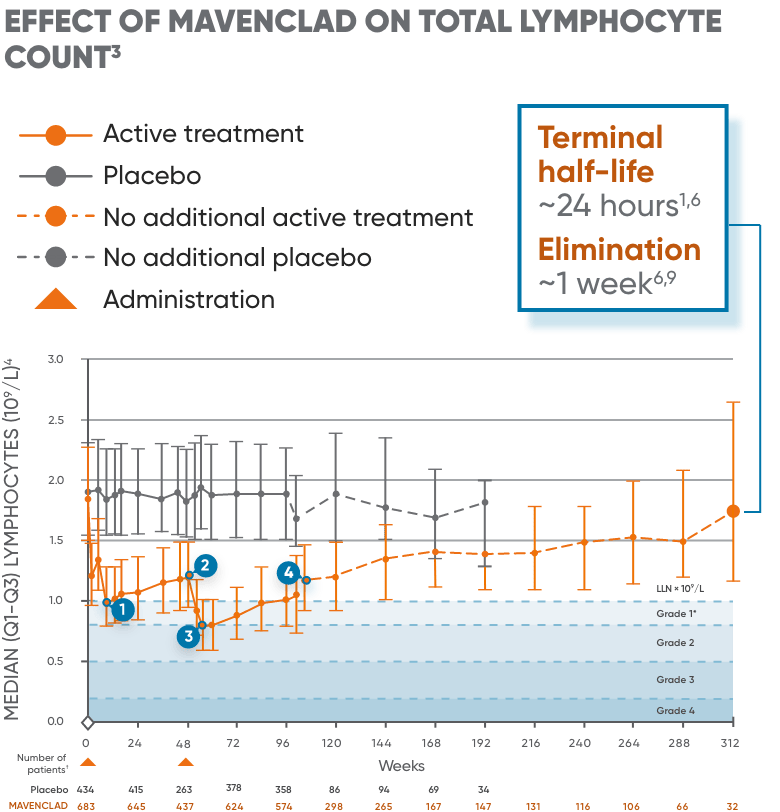
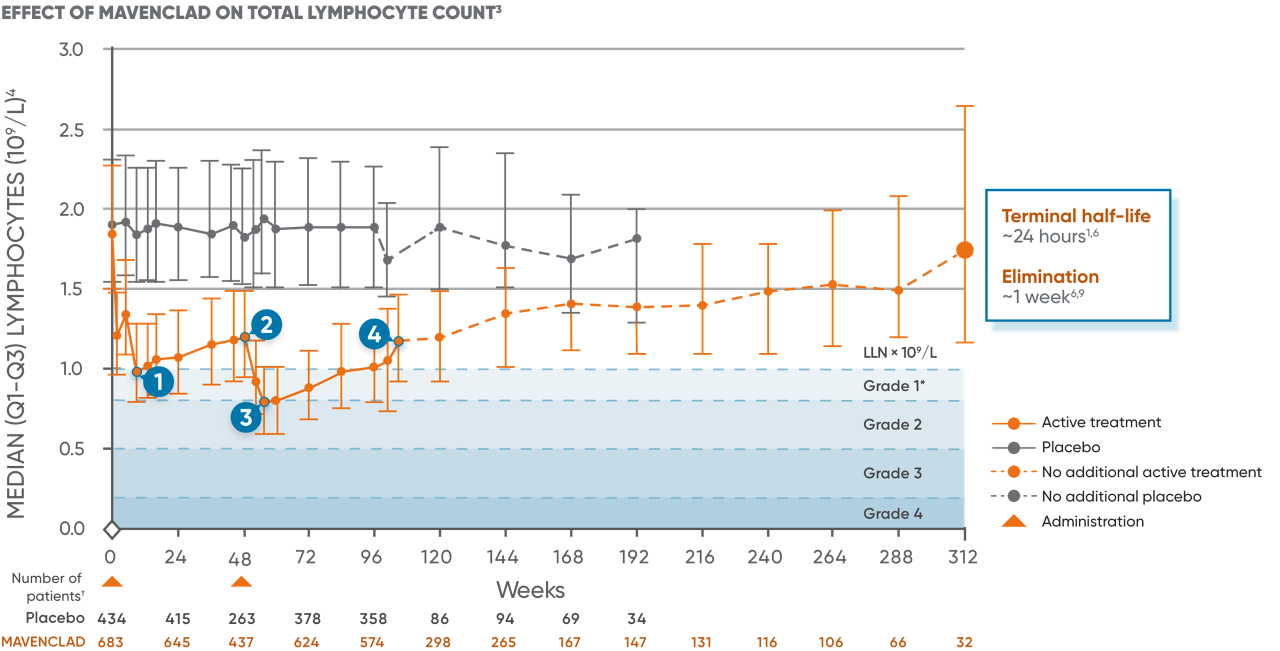
Lymphocyte counts were measured as part of routine clinical laboratory evaluations in patients in clinical studies.8 MAVENCLAD causes a dose-dependent reduction in lymphocyte count. In clinical studies, 87% of MAVENCLAD-treated patients experienced lymphopenia. The lowest absolute lymphocyte counts occurred approximately 2 to 3 months after the start of each treatment course and were lower with each additional treatment course.6
In patients treated with MAVENCLAD as monotherapy, lymphopenia observed was transient and mostly mild to moderate.8 The median duration of severe lymphopenia was 6.0 weeks to improvement to Grade ≤2 and 28.1 weeks to recovery to Grade ≤1.8 26% and 1% of patients had nadir absolute lymphocyte counts less than 500 and less than 200 cells/μL, respectively.6 At the end of the second treatment course, 2% of clinical study patients had lymphocyte counts less than 500 cells/μL.6